Loading Insight...
Insights
Insights

Intelligent automation combines RPA and AI, enabling rule-based robots to understand unstructured data and make predictions, expanding the scope of automation and improving stability and quality over time.
Intelligent automation, a powerful combination of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Artificial Intelligence (AI), is revolutionizing the automation landscape. In this article by Andrea Frauchiger, the impact of RPA and AI on automation agendas is explored. RPA has long been known for its ability to rapidly automate rule-based processes, but it has limitations when it comes to handling complex and ambiguous data. By integrating AI into RPA, organizations can leverage prediction-based models and enable robots to understand unstructured data, opening up new possibilities for automation and enhancing overall quality and stability. This article delves into the advantages of intelligent automation and highlights how it can transform businesses by automating a wider range of processes and achieving improved outcomes.
RPA: proven track record for fast-paced, rule-based automation
Robotic process automation (RPA) is a reliable and straightforward technology that allows the rule-based automation of business processes across any application. The fact that it’s non-invasive and can be quickly implemented in any IT architecture makes it very attractive in terms of costs and benefits and time to market.
At its core, automation with traditional RPA involves translating business requirements into a pre-defined rule set for processing structured data. The outcome is always binary: either a condition is met or it isn’t (static). There is no gray area with RPA.
Limitations of rule-based automation
Unfortunately for RPA, we have come across many business processes where the binary outcomes did not materialize fully, and a decision for a less favorable outcome − a lower automation rate − had to be made. A good example is KYC queries. The results presented to the compliance officer are rarely clear-cut black or white_,_ but mostly a «gray» area. Depending on the maturity of your RPA journey, this trend may be grounds for concern. With the increasing adoption of RPA automation, the use cases are tending to become more challenging, as the example below illustrates. As processes get more complex, the agility of RPA evaporates up to a point where putting the human back in the loop may be the only solution.
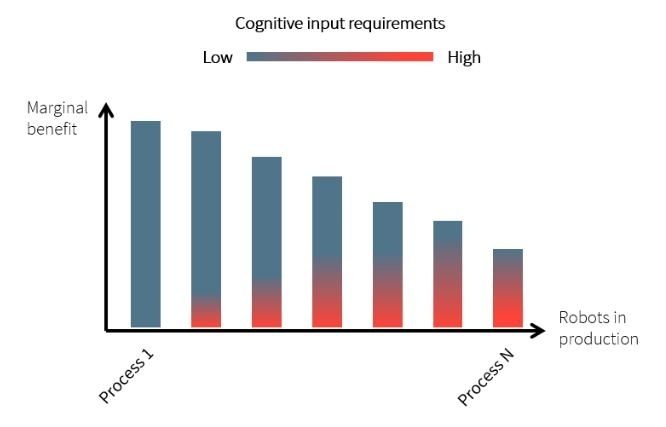
Figure 1: Higher cognitive input requirements impact the ROI of traditional RPA
AI-powered understanding instead of decision trees
The lack of cognitive skills for RPA automation in rule-based robots can be overcome with the help of artificial intelligence (AI). AI add-ons for RPA draw on prediction-based models which allow the robot to act based on a likelihood, thereby eliminating the need to program alternative complex and static decision trees.
Following a training phase (or an initial «big data» basis to train the algorithm), AI is able to support robotics in use cases ranging from invoice processing with digitized or scanned invoices and instructions up to the context-based output of unstructured text (e.g. a «full-text» email such as a complaint, general enquiry, etc.). This essentially allows robots to understand data that would otherwise not be usable without manual intervention or classification.
A further advantage of prediction-based models is that, under the right circumstances, they get better with time (whereas rule-based RPA is static). In the case of invoice processing, for instance, it could mean that future suppliers are automatically recognized and processed.

Figure 2: Traditional RPA struggles with understanding data. With AI, we can extend the reach of RPA in terms of the end-to-end automation spectrum.
Does an investment in cognitive skills pay off?
AI modules impact the RPA business case in terms of development costs and maintenance. The benefit can be showcased using a real-life process example.
In private banking, onboarding a new client requires the transfer of the client’s existing portfolio of assets. For this purpose, the old custodian bank issues so-called transfer instructions for the client’s portfolio. While the content of these instructions is standardized (security name, ISIN, quantity, and settlement instructions), the layout is not, meaning that the structure of the documents varies from bank to bank.
On the recipient bank’s side, this information is delivered by email and needs to be captured manually (or by a robot) in the core banking system. Without AI, an immense RPA decision tree would be required for each counterparty instruction layout, which is costly to develop and maintain. With AI, on the other hand, we can swap the decision tree for a prediction-based model that allows robots to understand the instructions and derive the required information.
The AI training of the model is both less sensitive to layout changes over time and cheaper than modeling a traditional RPA decision tree. This translates into increased benefits derived from less development time upfront and reduced maintenance.
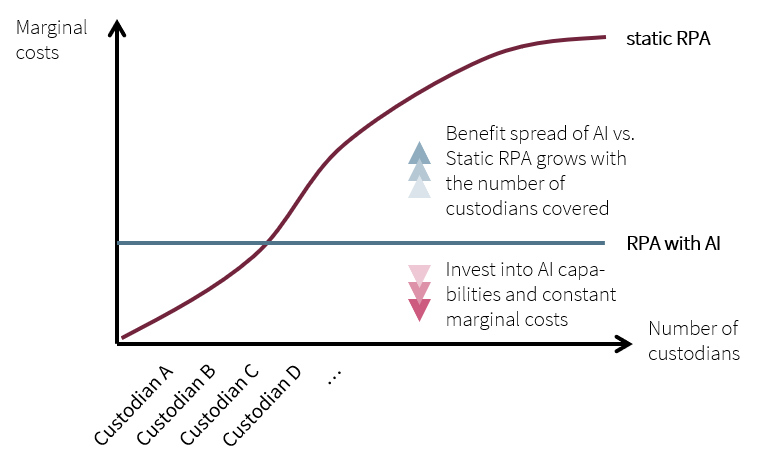
Figure 3: Cognitive robotics is more expensive upfront but pays off with growing business volume (example for the security transfer use case)
Being smart pays off
To maintain its position as a trusted agile automation tool, RPA will have to become smarter. In combination with AI, RPA achieves just that: unstructured data can be processed, extending the automation spectrum to processes or parts of processes previously out of reach.
Moreover, intelligent automation with AI is more resilient, and requires less maintenance over time owing to the learning capabilities of the AI models embedded in it.
In conclusion, adding AI to RPA allows you to automate more in terms of scope and achieve better quality and stability over time.
Ready to explore the potential of intelligent automation and discover how it can revolutionize your business processes? Contact our experts today to learn more and embark on a transformative automation journey. Gain insights, ask questions, and unlock the full potential of RPA and AI in your organization. Contact us now for more information!

Intelligent automation combines RPA and AI, enabling rule-based robots to understand unstructured data and make predictions, expanding the scope of automation and improving stability and quality over time.
Intelligent automation, a powerful combination of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Artificial Intelligence (AI), is revolutionizing the automation landscape. In this article by Andrea Frauchiger, the impact of RPA and AI on automation agendas is explored. RPA has long been known for its ability to rapidly automate rule-based processes, but it has limitations when it comes to handling complex and ambiguous data. By integrating AI into RPA, organizations can leverage prediction-based models and enable robots to understand unstructured data, opening up new possibilities for automation and enhancing overall quality and stability. This article delves into the advantages of intelligent automation and highlights how it can transform businesses by automating a wider range of processes and achieving improved outcomes.
RPA: proven track record for fast-paced, rule-based automation
Robotic process automation (RPA) is a reliable and straightforward technology that allows the rule-based automation of business processes across any application. The fact that it’s non-invasive and can be quickly implemented in any IT architecture makes it very attractive in terms of costs and benefits and time to market.
At its core, automation with traditional RPA involves translating business requirements into a pre-defined rule set for processing structured data. The outcome is always binary: either a condition is met or it isn’t (static). There is no gray area with RPA.
Limitations of rule-based automation
Unfortunately for RPA, we have come across many business processes where the binary outcomes did not materialize fully, and a decision for a less favorable outcome − a lower automation rate − had to be made. A good example is KYC queries. The results presented to the compliance officer are rarely clear-cut black or white_,_ but mostly a «gray» area. Depending on the maturity of your RPA journey, this trend may be grounds for concern. With the increasing adoption of RPA automation, the use cases are tending to become more challenging, as the example below illustrates. As processes get more complex, the agility of RPA evaporates up to a point where putting the human back in the loop may be the only solution.

Figure 1: Higher cognitive input requirements impact the ROI of traditional RPA
AI-powered understanding instead of decision trees
The lack of cognitive skills for RPA automation in rule-based robots can be overcome with the help of artificial intelligence (AI). AI add-ons for RPA draw on prediction-based models which allow the robot to act based on a likelihood, thereby eliminating the need to program alternative complex and static decision trees.
Following a training phase (or an initial «big data» basis to train the algorithm), AI is able to support robotics in use cases ranging from invoice processing with digitized or scanned invoices and instructions up to the context-based output of unstructured text (e.g. a «full-text» email such as a complaint, general enquiry, etc.). This essentially allows robots to understand data that would otherwise not be usable without manual intervention or classification.
A further advantage of prediction-based models is that, under the right circumstances, they get better with time (whereas rule-based RPA is static). In the case of invoice processing, for instance, it could mean that future suppliers are automatically recognized and processed.

Figure 2: Traditional RPA struggles with understanding data. With AI, we can extend the reach of RPA in terms of the end-to-end automation spectrum.
Does an investment in cognitive skills pay off?
AI modules impact the RPA business case in terms of development costs and maintenance. The benefit can be showcased using a real-life process example.
In private banking, onboarding a new client requires the transfer of the client’s existing portfolio of assets. For this purpose, the old custodian bank issues so-called transfer instructions for the client’s portfolio. While the content of these instructions is standardized (security name, ISIN, quantity, and settlement instructions), the layout is not, meaning that the structure of the documents varies from bank to bank.
On the recipient bank’s side, this information is delivered by email and needs to be captured manually (or by a robot) in the core banking system. Without AI, an immense RPA decision tree would be required for each counterparty instruction layout, which is costly to develop and maintain. With AI, on the other hand, we can swap the decision tree for a prediction-based model that allows robots to understand the instructions and derive the required information.
The AI training of the model is both less sensitive to layout changes over time and cheaper than modeling a traditional RPA decision tree. This translates into increased benefits derived from less development time upfront and reduced maintenance.

Figure 3: Cognitive robotics is more expensive upfront but pays off with growing business volume (example for the security transfer use case)
Being smart pays off
To maintain its position as a trusted agile automation tool, RPA will have to become smarter. In combination with AI, RPA achieves just that: unstructured data can be processed, extending the automation spectrum to processes or parts of processes previously out of reach.
Moreover, intelligent automation with AI is more resilient, and requires less maintenance over time owing to the learning capabilities of the AI models embedded in it.
In conclusion, adding AI to RPA allows you to automate more in terms of scope and achieve better quality and stability over time.
Ready to explore the potential of intelligent automation and discover how it can revolutionize your business processes? Contact our experts today to learn more and embark on a transformative automation journey. Gain insights, ask questions, and unlock the full potential of RPA and AI in your organization. Contact us now for more information!




