Loading Insight...
Insights
Insights

The global trade finance market is poised for an additional 5.4%1 growth, presenting opportunities for those who serve the underbanked. We look at the key opportunities and challenges when lending to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
Recent reports have shown that the Asia Pacific region dominates the global trade finance market, with Hong Kong and China alone making up 56% of inward FAT sales.2 Moreover, the industry is poised for an additional 5.4% growth between 2022 and 2028, representing vast opportunities for those who serve the underbanked.[1]

Figure 1: Overview of global trade finance market[²]
What are the key opportunities and challenges banks face when inclusive lending to SMEs? How should they rethink the traditional credit model?
Sustainability, innovation, and inclusiveness are key drivers for growth
A renewed focus on customer experience, sustainability, and inclusiveness is necessary for banks to grow business. Here are some important considerations when shifting to a new banking model.
The journey toward sustainable banking
While the world continues its search for a standardised approach to ESG ratings, 80% of senior management consider these ratings as important for industry. A push for the “Green Asset Ratio” in European banks is likely to follow in Asia.
Inclusive supply chain financing for SMEs
60% of trade finance requests are rejected, with SME customers suffering the most due to higher rates of non-performing loans. While SMEs have often been excluded from supply chain financing, governments are actively remedying this with policies and regulations to assist the underbanked, which will require more intuitive credit assessment and streamlined processes. In other words, if banks don’t satisfy the credit needs of SME clients they will find it elsewhere.
Rethinking credit for sustainability
Businesses are facing a substantial impact on their credit with the introduction of carbon taxes across the globe. As a result, banks are implementing avoidance policies. However, issues such as stress testing, greenwashing, and fraud still require updated policies, automation, and training.
SMEs need assistance to help them adapt to the green economy and banks can assist in that development.
Roong Mallikamas Assistant Governor, Financial Institutions Policy, Bank of Thailand
ESG lending also remains a key challenge for banks and adopting a wait-and-see approach may seem tempting. However, establishing the right framework that allows for an evolving market is essential so that banks can deliver profitable, ESG-compliant, lending that furthers social improvement.
Loans are a key source of financing across Asia - be it for individuals, SMEs or large corporates. Therefore, there is significant opportunity to encourage firms across different industries to transition to more sustainable practices through green and sustainability-linked loans.”
Ravi Menon Managing Director, Monetary Authority of Singapore
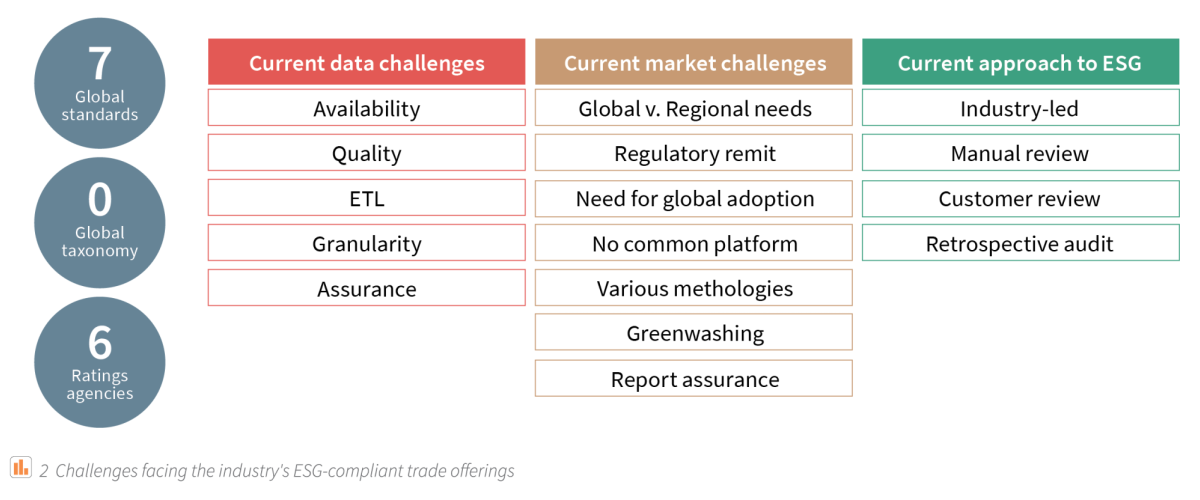
Figure 2: Challenges facing the industry's ESG-compliant trade offerings
Data is an undervalued commodity in trade financing
Whether it’s predictive credit limits, enhanced credit analytics, or powerful customer insights, data is the backbone of any meaningful client offering. Unfortunately, banks often still struggle to produce data that is reliable and consistent with their existing in-house technology architecture. Creating a culture of data-driven insights and analytics to inform the bank’s credit decisions and engage with customers is paramount to an agile, evolving corporate bank.
Is Open Banking a threat or an opportunity?
Corporate banks need to act on customer and market expectations to ensure a net benefit to Open Banking. Because customers are likely to “vote with their feet,”banks that offer the best customer experience will win the race. With new customer acquisition cost averaging between USD 100 to USD 200, banks will need to strengthen their existing client base on top of onboarding new customers. Banks should start investing in their customer’s financial journeys now to remain competitive in this space.
The HKMA (Hong Kong Monetary Authority) will continue to facilitate the strengthening of trust across all banking Open API (Application Programming Interface) participants and promote a healthy ecosystem conducive to financial innovation.
Howard Lee, JP Deputy Chief Executive, Hong Kong Monetary Authority
How digitalisation can improve a bank’s end-to-end trade finance capabilities
Trade finance presents a unique challenge for regulators since a trade finance transaction typically involves multiple jurisdictions. Financial institutions are looking at ways to digitise more of their end-to-end trade finance capabilities. For a bank to achieve its strategic growth goals, it should prioritise partnerships with authenticated vendors. Here are the specific advantages of digitizing your bank’s end-to-end trade finance capabilities.
Automation makes trade finance processes more efficient
Manual trade finance processes are less reliable because the margin for human error is much higher. When these processes are digitised, banks can better manage transactions and workflow.
Get the right data to make better decisions
Data is an essential but frequently overlooked part of corporate banking. Whether you’re conducting an ESG audit or offering customers meaningful insights, you need to make sure that your bank’s data is correct. Having a secure automated system allows workers to access customer data without breaking a sweat.
Sustainability should be ‘BAU’ rather than a separate initiative
Trade clients as well as banks are facing increased pressure to comply with global standards for ESG. Definitions are evolving, and the availability of data remains a key challenge. There should be renewed focus on creating an ESG framework that’s both feasible and measurable to ensure future compliance and agility to regulation.
Create a private bank-like service for corporate customers
Importers and exporters are seeking more information and insights about their lending facilities, trade activities, and relevant risks, and may be willing to pay a premium for it.
The trade lifecycle outlined in Figure 3 highlights several key areas for innovation. It shows the traditional credit model and the market trends that might improve these processes. Thanks to technological advances in finance trading, lenders are able to derive meaningful insights into borrower behaviour and credit events. Tools such as machine learning and automated monitoring can streamline manual trade processes, which allow financial institutions to keep up with macro-economic developments, stay competitive with non-bank lenders, and comply with tightening regulations.
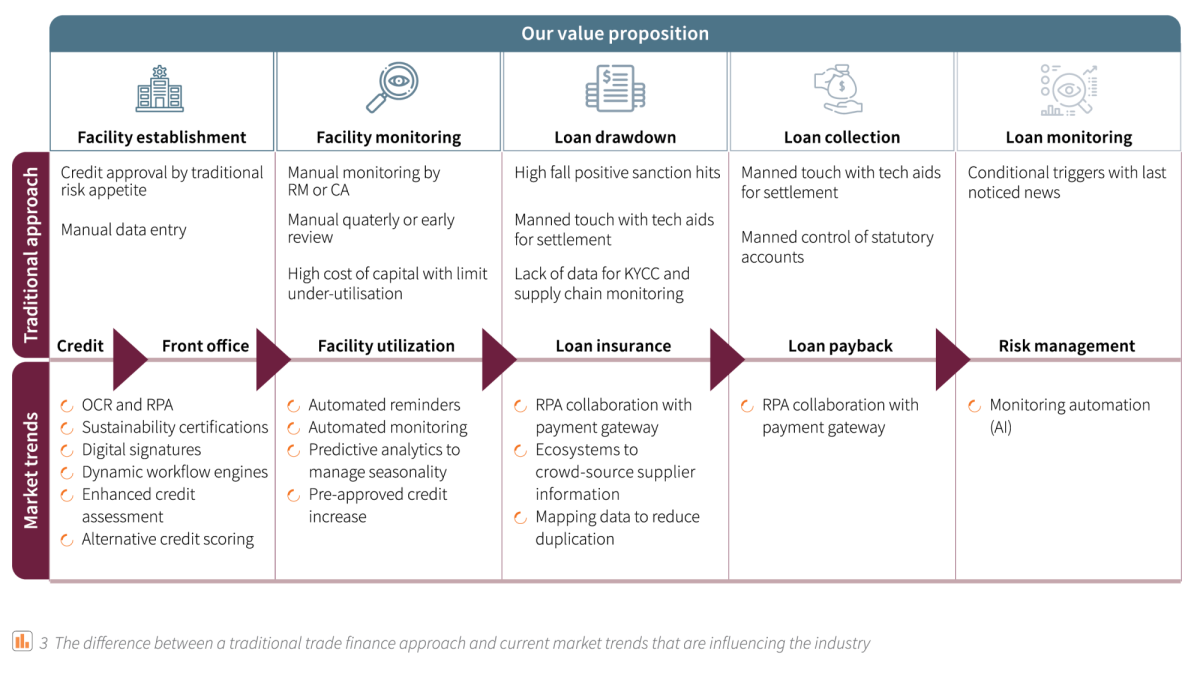
Figure 3: The difference between a traditional trade finance approach and current market trends that are influencing the industry
Compared to the traditional approach, digitalisation appears to offer lower costs, fewer errors, and quicker approval. Standardised digital platforms can help lenders manage their workflow and facilitate collaboration between trade financial functions within the bank. These platforms also provide a structure for trade finance providers to easily access documents in large data pools to reap the benefits of data analytics. Robotic process automation (RPA) like automated reminders and automated monitoring can free up valuable time for workers to focus on other tasks. Digitalisation doesn’t only accelerate credit processes, but it also enables banks to utilize application programming interfaces (APIs) and access blockchain platforms in the wider trade ecosystem7.
What Synpulse can do for you
Building a new trade finance model can take years if you don’t have the proper tools and expertise. Synpulse can help you navigate this stage in your bank’s development with innovative end-to-end solutions.
1 Trade Finance Market USD 11631260 Million By 2028 With A CAGR of 5.4% - Valuates Reports. [Link: https://eur01.safelinks.protec...] 2 World Trade Organization (WTO). World Trade Statistical Review 2018. [Link: https://www.wto.org/english/re...] 3 WTO. IFC-WTO event: “Financial inclusion in trade: Reducing the global trade finance gap”. 9 October 2018. [Link: https://www.wto.org/english/ne....] 4 Bangkok Post. Green lending under BoT scrutiny. 24 August 2022. [Link: https://www.bangkokpost.com/bu...] 5 The Straits Times. MAS launches world's first grant scheme for green and sustainability-linked loans. 24 November 2020. [Link: https://www.straitstimes.com/business/banking/mas-debuts-grant-scheme-to-support-green-and-sustainability-linked-loans] 6 HKMA. The implementation plan for Phase III and IV Open Application Programming Interface (Open API). 13 May 2021. [Link: https://www.hkma.gov.hk/eng/ne...] 7 Köller & Amerongen. The Shaping of Modern Trade Finance Services. May 6, 2019. [Link: https://themagazine.synpulse.c...]

The global trade finance market is poised for an additional 5.4%1 growth, presenting opportunities for those who serve the underbanked. We look at the key opportunities and challenges when lending to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
Recent reports have shown that the Asia Pacific region dominates the global trade finance market, with Hong Kong and China alone making up 56% of inward FAT sales.2 Moreover, the industry is poised for an additional 5.4% growth between 2022 and 2028, representing vast opportunities for those who serve the underbanked.[1]

Figure 1: Overview of global trade finance market[²]
What are the key opportunities and challenges banks face when inclusive lending to SMEs? How should they rethink the traditional credit model?
Sustainability, innovation, and inclusiveness are key drivers for growth
A renewed focus on customer experience, sustainability, and inclusiveness is necessary for banks to grow business. Here are some important considerations when shifting to a new banking model.
The journey toward sustainable banking
While the world continues its search for a standardised approach to ESG ratings, 80% of senior management consider these ratings as important for industry. A push for the “Green Asset Ratio” in European banks is likely to follow in Asia.
Inclusive supply chain financing for SMEs
60% of trade finance requests are rejected, with SME customers suffering the most due to higher rates of non-performing loans. While SMEs have often been excluded from supply chain financing, governments are actively remedying this with policies and regulations to assist the underbanked, which will require more intuitive credit assessment and streamlined processes. In other words, if banks don’t satisfy the credit needs of SME clients they will find it elsewhere.
Rethinking credit for sustainability
Businesses are facing a substantial impact on their credit with the introduction of carbon taxes across the globe. As a result, banks are implementing avoidance policies. However, issues such as stress testing, greenwashing, and fraud still require updated policies, automation, and training.
SMEs need assistance to help them adapt to the green economy and banks can assist in that development.
Roong Mallikamas Assistant Governor, Financial Institutions Policy, Bank of Thailand
ESG lending also remains a key challenge for banks and adopting a wait-and-see approach may seem tempting. However, establishing the right framework that allows for an evolving market is essential so that banks can deliver profitable, ESG-compliant, lending that furthers social improvement.
Loans are a key source of financing across Asia - be it for individuals, SMEs or large corporates. Therefore, there is significant opportunity to encourage firms across different industries to transition to more sustainable practices through green and sustainability-linked loans.”
Ravi Menon Managing Director, Monetary Authority of Singapore

Figure 2: Challenges facing the industry's ESG-compliant trade offerings
Data is an undervalued commodity in trade financing
Whether it’s predictive credit limits, enhanced credit analytics, or powerful customer insights, data is the backbone of any meaningful client offering. Unfortunately, banks often still struggle to produce data that is reliable and consistent with their existing in-house technology architecture. Creating a culture of data-driven insights and analytics to inform the bank’s credit decisions and engage with customers is paramount to an agile, evolving corporate bank.
Is Open Banking a threat or an opportunity?
Corporate banks need to act on customer and market expectations to ensure a net benefit to Open Banking. Because customers are likely to “vote with their feet,”banks that offer the best customer experience will win the race. With new customer acquisition cost averaging between USD 100 to USD 200, banks will need to strengthen their existing client base on top of onboarding new customers. Banks should start investing in their customer’s financial journeys now to remain competitive in this space.
The HKMA (Hong Kong Monetary Authority) will continue to facilitate the strengthening of trust across all banking Open API (Application Programming Interface) participants and promote a healthy ecosystem conducive to financial innovation.
Howard Lee, JP Deputy Chief Executive, Hong Kong Monetary Authority
How digitalisation can improve a bank’s end-to-end trade finance capabilities
Trade finance presents a unique challenge for regulators since a trade finance transaction typically involves multiple jurisdictions. Financial institutions are looking at ways to digitise more of their end-to-end trade finance capabilities. For a bank to achieve its strategic growth goals, it should prioritise partnerships with authenticated vendors. Here are the specific advantages of digitizing your bank’s end-to-end trade finance capabilities.
Automation makes trade finance processes more efficient
Manual trade finance processes are less reliable because the margin for human error is much higher. When these processes are digitised, banks can better manage transactions and workflow.
Get the right data to make better decisions
Data is an essential but frequently overlooked part of corporate banking. Whether you’re conducting an ESG audit or offering customers meaningful insights, you need to make sure that your bank’s data is correct. Having a secure automated system allows workers to access customer data without breaking a sweat.
Sustainability should be ‘BAU’ rather than a separate initiative
Trade clients as well as banks are facing increased pressure to comply with global standards for ESG. Definitions are evolving, and the availability of data remains a key challenge. There should be renewed focus on creating an ESG framework that’s both feasible and measurable to ensure future compliance and agility to regulation.
Create a private bank-like service for corporate customers
Importers and exporters are seeking more information and insights about their lending facilities, trade activities, and relevant risks, and may be willing to pay a premium for it.
The trade lifecycle outlined in Figure 3 highlights several key areas for innovation. It shows the traditional credit model and the market trends that might improve these processes. Thanks to technological advances in finance trading, lenders are able to derive meaningful insights into borrower behaviour and credit events. Tools such as machine learning and automated monitoring can streamline manual trade processes, which allow financial institutions to keep up with macro-economic developments, stay competitive with non-bank lenders, and comply with tightening regulations.

Figure 3: The difference between a traditional trade finance approach and current market trends that are influencing the industry
Compared to the traditional approach, digitalisation appears to offer lower costs, fewer errors, and quicker approval. Standardised digital platforms can help lenders manage their workflow and facilitate collaboration between trade financial functions within the bank. These platforms also provide a structure for trade finance providers to easily access documents in large data pools to reap the benefits of data analytics. Robotic process automation (RPA) like automated reminders and automated monitoring can free up valuable time for workers to focus on other tasks. Digitalisation doesn’t only accelerate credit processes, but it also enables banks to utilize application programming interfaces (APIs) and access blockchain platforms in the wider trade ecosystem7.
What Synpulse can do for you
Building a new trade finance model can take years if you don’t have the proper tools and expertise. Synpulse can help you navigate this stage in your bank’s development with innovative end-to-end solutions.
1 Trade Finance Market USD 11631260 Million By 2028 With A CAGR of 5.4% - Valuates Reports. [Link: https://eur01.safelinks.protec...] 2 World Trade Organization (WTO). World Trade Statistical Review 2018. [Link: https://www.wto.org/english/re...] 3 WTO. IFC-WTO event: “Financial inclusion in trade: Reducing the global trade finance gap”. 9 October 2018. [Link: https://www.wto.org/english/ne....] 4 Bangkok Post. Green lending under BoT scrutiny. 24 August 2022. [Link: https://www.bangkokpost.com/bu...] 5 The Straits Times. MAS launches world's first grant scheme for green and sustainability-linked loans. 24 November 2020. [Link: https://www.straitstimes.com/business/banking/mas-debuts-grant-scheme-to-support-green-and-sustainability-linked-loans] 6 HKMA. The implementation plan for Phase III and IV Open Application Programming Interface (Open API). 13 May 2021. [Link: https://www.hkma.gov.hk/eng/ne...] 7 Köller & Amerongen. The Shaping of Modern Trade Finance Services. May 6, 2019. [Link: https://themagazine.synpulse.c...]





