Loading Insight...
Insights
Insights

Summary
- GenAI can address inefficiencies in underwriting, especially in processing unstructured data from commercial lines and reinsurance.
- Underwriting challenges include manual tasks, inconsistent decision-making, and fragmented data, which impact efficiency and accuracy.
- GenAI surpasses traditional AI/ML by handling unstructured data, enabling automated risk evaluation, document extraction, and smart triaging.
- Successful GenAI adoption requires robust infrastructure, centralised data assets, and well-defined governance for data and models.
- End-to-end GenAI integration can reduce manual interventions, improve underwriting accuracy, and drive strategic advantages in pricing and customer experience.
For years, the insurance industry has been regarded as being on the cusp of disruption. While this transformation has yet to fully materialise, the rapid advancements in generative AI (GenAI), which began with the release of GPT-3.5 in late 2022, offer a new perspective for industry futurists.
As insurers contend with challenges such as inefficient processes, inconsistent decision-making, and the underutilisation of data locked in unstructured documents, GenAI presents a transformative opportunity for underwriting operations. This is especially relevant in commercial lines and reinsurance, where the complexity of risks has traditionally resisted standardisation. The significant volume of unstructured data in these areas still demands a heavily human-driven underwriting approach, making GenAI an ideal solution to revolutionise this process.
Deconstructing the underwriting process
To understand the impact of GenAI on underwriting, we must first examine the underwriting value chain using large commercial lines, such as directors and officers (D&O) liability and general casualty, as examples.
Throughout the process, underwriters face several challenges that impede both efficiency and effectiveness (see Table 2). Manual, repetitive tasks such as data entry and document review consume a significant portion of their time. Inconsistent risk assessment and decision-making, often stemming from a reliance on individual judgement and limited data, can result in suboptimal outcomes. The lack of integration between disparate data sources and systems exacerbates these issues, making it difficult to gain a comprehensive view of risks and make well-informed decisions.
Furthermore, the increasing complexity of risks and regulations in specialty lines and reinsurance adds another layer of difficulty. Underwriters must navigate numerous coverage options, exclusions, and endorsements, while also ensuring compliance with evolving regulatory requirements. These time-consuming tasks not only increase operational costs but also delay the quote-to-bind process, negatively impacting customer experience and competitiveness.
Across the various stages of the underwriting value chain—both for new business and renewals—there are varying degrees of manual effort, inefficiencies, and inconsistencies. A snapshot of these challenges can be seen in Table 1:
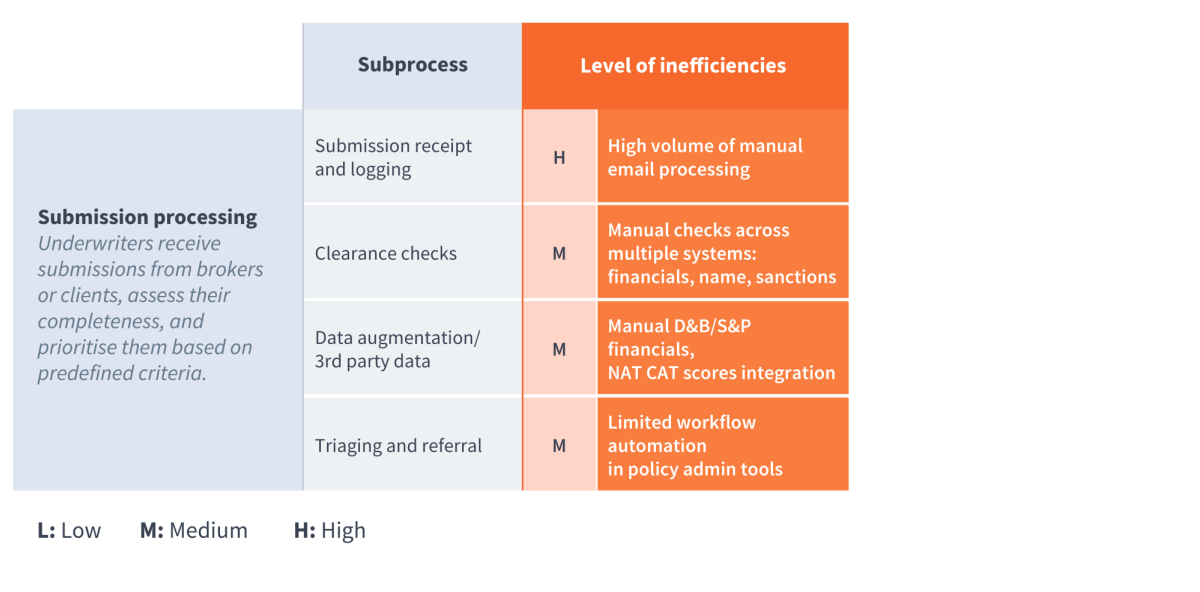
Table 1: An example of inefficiencies across the various stages of the underwriting value chain. For the full view, please refer to Table 2 further down below.
The GenAI advantage: beyond traditional AI/ML
Traditional AI and machine learning (AI/ML) approaches have been applied to address some of these challenges, but we can now admit that their effectiveness has been limited. Because these techniques often rely on identifying patterns in large volumes of structured historical data, they can be ill-suited to the unstructured and dynamic nature of underwriting data. These techniques also require extensive training and fine-tuning for each specific use case, which leads, where sufficient data volumes even exist, to long implementation cycles and high maintenance costs.
GenAI, and Large Language Models (LLMs) in particular, offers a paradigm shift in our approach to using AI within underwriting (among others). LLMs are pre-trained on vast amounts of diverse data, enabling them to “understand” and generate human-like text with remarkable coherence and contextual awareness. This allows GenAI models to handle unstructured data, such as submission documents, emails, and reports, without the need for manual preprocessing or feature engineering. As a result, GenAI solutions can be deployed across multiple stages of the underwriting process, from data extraction to risk evaluation and review of policy wording.
A framework for deploying GenAI in underwriting
To harness the potential of GenAI in underwriting, it is useful to analyse what models can do, that is the patterns by which they interact with data when deployed against specific tasks. We will use our framework from our previously published whitepaper.
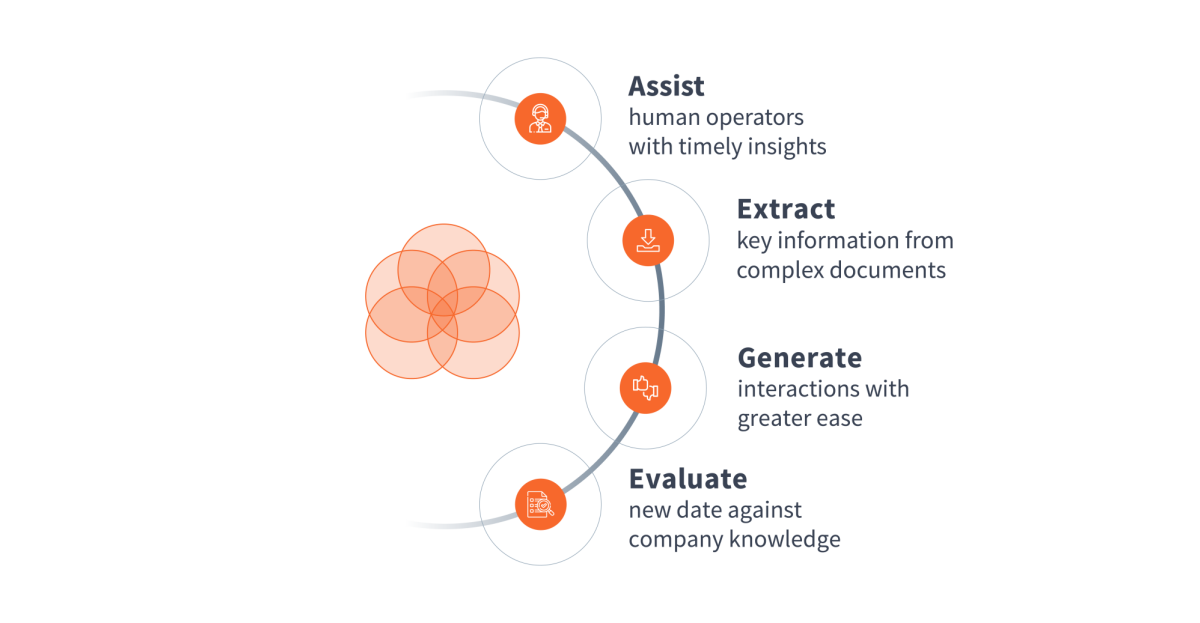
Picture capture: Only a few teams have moved from theoretical exploration to practical implementation, and even fewer are actively exploring use cases with real transformational potential. Those who lead the way and actively engage with extraction and evaluation patterns are more likely to rapidly accumulate learning and reap the rewards of deep transformations.
Unlocking process transformation potential
In this current era of insurance underwriting, the current application of AI is predominantly using Traditional AI/ML methodologies and concentrated in specific areas of the underwriting value chain. These focus areas include submission logging and triaging, appetite checking, data retrieval for renewals processing and GPT-4-mainly being used for searches.
While these areas have seen some considerable advancements, the potential for GenAI’s transformative impact extends far beyond these applications. Opportunities for further GenAI intervention exist across a broader spectrum of underwriting operations, which include, but are not limited to, areas such as follows:
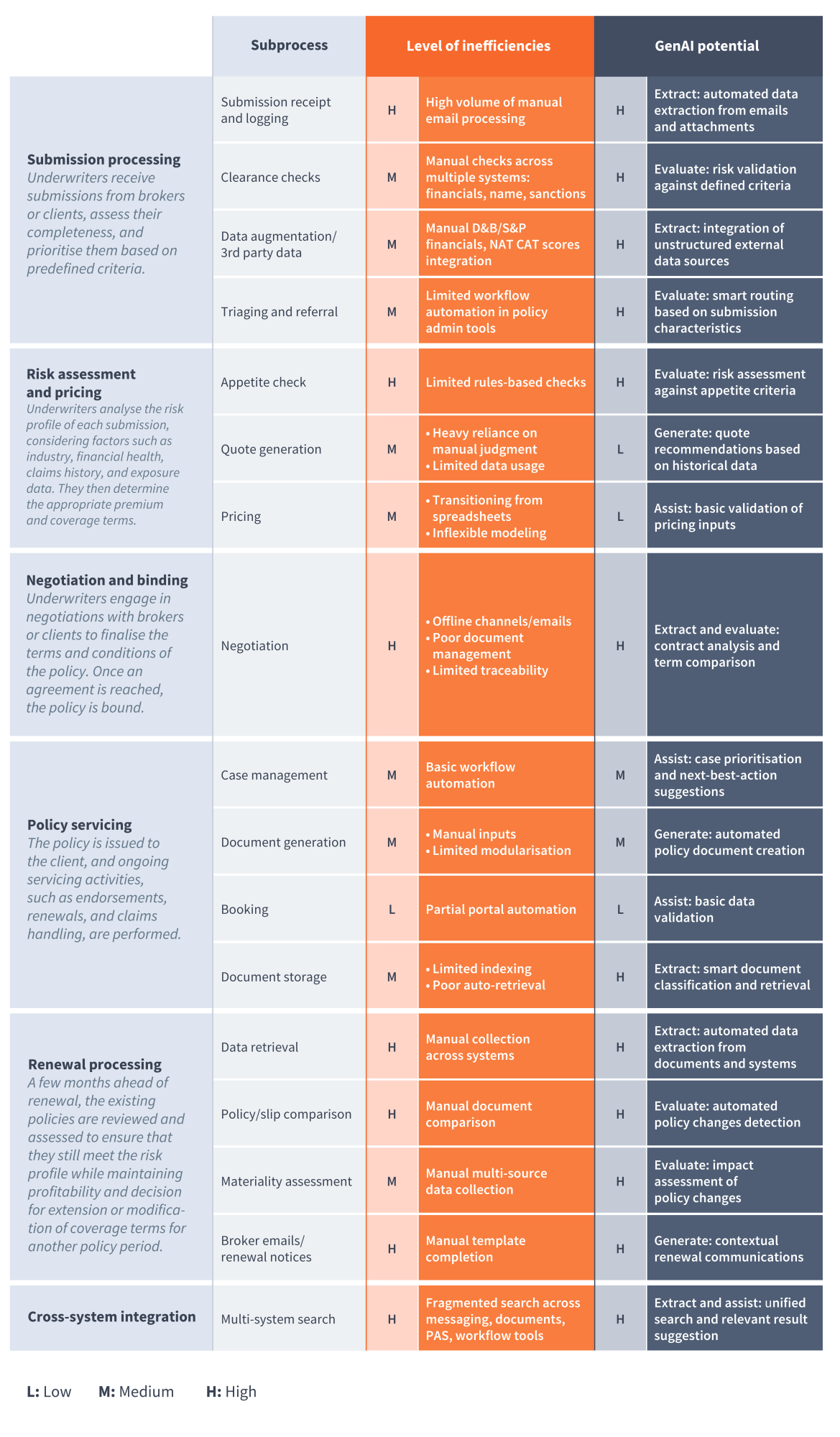
Table 2: GenAI potential across the various stages of the underwriting value chain
GenAI in underwriting operations offers insurers a transformative opportunity to accelerate digital transformation across their entire value chain. By automating data extraction and structuring from diverse sources, GenAI enables a unified view of risks and exposures across portfolios, improving risk assessment accuracy and portfolio optimization. Moreover, GenAI-driven insights can inform strategic decision-making, such as product development and pricing strategies, helping insurers stay ahead of the competition.
While individual process improvements yield benefits, GenAI's true potential lies in creating end-to-end automated workflows that minimize manual interventions and bottlenecks. This comprehensive integration not only enhances operational efficiency and reduces costs but also drives strategic advantages in product development and pricing, ultimately improving customer experience and regulatory compliance.
At the moment, we do not believe that GenAI model can quite replace underwriters, at least for large and complex risks. This hesitation stems not only from GenAI’s variable performance regarding an ever-evolving set of inputs but also from its inability to assume accountability if underwriting decisions go awry. However, this does not mean that the underwriting process will remain unchanged in the coming years. As underwriters focus on areas where they can add the most value, they are likely to delegate more routine tasks to machines. For instance, we anticipate that risk information will be extracted, enriched, and compared against company guidelines, with auto-pricing conducted before the information is even presented to the underwriter. This process will likely be facilitated by sophisticated triaging algorithms.
![]()
By reimagining underwriting processes around GenAI capabilities, insurers can unlock significant efficiency gains, reduce cycle times, and improve the overall quality and consistency of underwriting decisions. However, it will require a fundamental shift in how we think about process design and optimisation. Rather than simply automating existing processes, insurers must take a holistic view of the underwriting value chain and identify opportunities for process simplification, standardisation, and integration. This might involve breaking down silos between different functions, redesigning workflows to leverage GenAI capabilities, and establishing clear governance on what types of decisions can or cannot be delegated to AI.
Building the foundation for GenAI-driven underwriting
Successful GenAI adoption requires careful planning and strategic execution. Insurers must first assess their organizational readiness and develop a clear strategy aligned with business objectives. This includes prioritizing high-impact use cases and establishing a secure environment for iterative testing and scaling. The effective utilization of GenAI fundamentally depends on robust foundational capabilities: a sophisticated technical infrastructure, comprehensive central data assets, well-defined governance frameworks for both data and models, targeted talent development, and a clear operating model for data and AI initiatives.
By taking a holistic approach to GenAI adoption, insurers can drive operational efficiency and unlock new growth opportunities in the digital age. Success begins with a bold vision and willingness to embrace this transformative technology. Those who proactively invest in building strong foundations and necessary capabilities will be best positioned to realize GenAI's full potential in underwriting transformation.
Want to know more about how to leverage GenAI for underwriting operations? Learn more about our GenAI services on our website.

Summary
- GenAI can address inefficiencies in underwriting, especially in processing unstructured data from commercial lines and reinsurance.
- Underwriting challenges include manual tasks, inconsistent decision-making, and fragmented data, which impact efficiency and accuracy.
- GenAI surpasses traditional AI/ML by handling unstructured data, enabling automated risk evaluation, document extraction, and smart triaging.
- Successful GenAI adoption requires robust infrastructure, centralised data assets, and well-defined governance for data and models.
- End-to-end GenAI integration can reduce manual interventions, improve underwriting accuracy, and drive strategic advantages in pricing and customer experience.
For years, the insurance industry has been regarded as being on the cusp of disruption. While this transformation has yet to fully materialise, the rapid advancements in generative AI (GenAI), which began with the release of GPT-3.5 in late 2022, offer a new perspective for industry futurists.
As insurers contend with challenges such as inefficient processes, inconsistent decision-making, and the underutilisation of data locked in unstructured documents, GenAI presents a transformative opportunity for underwriting operations. This is especially relevant in commercial lines and reinsurance, where the complexity of risks has traditionally resisted standardisation. The significant volume of unstructured data in these areas still demands a heavily human-driven underwriting approach, making GenAI an ideal solution to revolutionise this process.
Deconstructing the underwriting process
To understand the impact of GenAI on underwriting, we must first examine the underwriting value chain using large commercial lines, such as directors and officers (D&O) liability and general casualty, as examples.
Throughout the process, underwriters face several challenges that impede both efficiency and effectiveness (see Table 2). Manual, repetitive tasks such as data entry and document review consume a significant portion of their time. Inconsistent risk assessment and decision-making, often stemming from a reliance on individual judgement and limited data, can result in suboptimal outcomes. The lack of integration between disparate data sources and systems exacerbates these issues, making it difficult to gain a comprehensive view of risks and make well-informed decisions.
Furthermore, the increasing complexity of risks and regulations in specialty lines and reinsurance adds another layer of difficulty. Underwriters must navigate numerous coverage options, exclusions, and endorsements, while also ensuring compliance with evolving regulatory requirements. These time-consuming tasks not only increase operational costs but also delay the quote-to-bind process, negatively impacting customer experience and competitiveness.
Across the various stages of the underwriting value chain—both for new business and renewals—there are varying degrees of manual effort, inefficiencies, and inconsistencies. A snapshot of these challenges can be seen in Table 1:

Table 1: An example of inefficiencies across the various stages of the underwriting value chain. For the full view, please refer to Table 2 further down below.
The GenAI advantage: beyond traditional AI/ML
Traditional AI and machine learning (AI/ML) approaches have been applied to address some of these challenges, but we can now admit that their effectiveness has been limited. Because these techniques often rely on identifying patterns in large volumes of structured historical data, they can be ill-suited to the unstructured and dynamic nature of underwriting data. These techniques also require extensive training and fine-tuning for each specific use case, which leads, where sufficient data volumes even exist, to long implementation cycles and high maintenance costs.
GenAI, and Large Language Models (LLMs) in particular, offers a paradigm shift in our approach to using AI within underwriting (among others). LLMs are pre-trained on vast amounts of diverse data, enabling them to “understand” and generate human-like text with remarkable coherence and contextual awareness. This allows GenAI models to handle unstructured data, such as submission documents, emails, and reports, without the need for manual preprocessing or feature engineering. As a result, GenAI solutions can be deployed across multiple stages of the underwriting process, from data extraction to risk evaluation and review of policy wording.
A framework for deploying GenAI in underwriting
To harness the potential of GenAI in underwriting, it is useful to analyse what models can do, that is the patterns by which they interact with data when deployed against specific tasks. We will use our framework from our previously published whitepaper.

Picture capture: Only a few teams have moved from theoretical exploration to practical implementation, and even fewer are actively exploring use cases with real transformational potential. Those who lead the way and actively engage with extraction and evaluation patterns are more likely to rapidly accumulate learning and reap the rewards of deep transformations.
Unlocking process transformation potential
In this current era of insurance underwriting, the current application of AI is predominantly using Traditional AI/ML methodologies and concentrated in specific areas of the underwriting value chain. These focus areas include submission logging and triaging, appetite checking, data retrieval for renewals processing and GPT-4-mainly being used for searches.
While these areas have seen some considerable advancements, the potential for GenAI’s transformative impact extends far beyond these applications. Opportunities for further GenAI intervention exist across a broader spectrum of underwriting operations, which include, but are not limited to, areas such as follows:

Table 2: GenAI potential across the various stages of the underwriting value chain
GenAI in underwriting operations offers insurers a transformative opportunity to accelerate digital transformation across their entire value chain. By automating data extraction and structuring from diverse sources, GenAI enables a unified view of risks and exposures across portfolios, improving risk assessment accuracy and portfolio optimization. Moreover, GenAI-driven insights can inform strategic decision-making, such as product development and pricing strategies, helping insurers stay ahead of the competition.
While individual process improvements yield benefits, GenAI's true potential lies in creating end-to-end automated workflows that minimize manual interventions and bottlenecks. This comprehensive integration not only enhances operational efficiency and reduces costs but also drives strategic advantages in product development and pricing, ultimately improving customer experience and regulatory compliance.
At the moment, we do not believe that GenAI model can quite replace underwriters, at least for large and complex risks. This hesitation stems not only from GenAI’s variable performance regarding an ever-evolving set of inputs but also from its inability to assume accountability if underwriting decisions go awry. However, this does not mean that the underwriting process will remain unchanged in the coming years. As underwriters focus on areas where they can add the most value, they are likely to delegate more routine tasks to machines. For instance, we anticipate that risk information will be extracted, enriched, and compared against company guidelines, with auto-pricing conducted before the information is even presented to the underwriter. This process will likely be facilitated by sophisticated triaging algorithms.
![]()
By reimagining underwriting processes around GenAI capabilities, insurers can unlock significant efficiency gains, reduce cycle times, and improve the overall quality and consistency of underwriting decisions. However, it will require a fundamental shift in how we think about process design and optimisation. Rather than simply automating existing processes, insurers must take a holistic view of the underwriting value chain and identify opportunities for process simplification, standardisation, and integration. This might involve breaking down silos between different functions, redesigning workflows to leverage GenAI capabilities, and establishing clear governance on what types of decisions can or cannot be delegated to AI.
Building the foundation for GenAI-driven underwriting
Successful GenAI adoption requires careful planning and strategic execution. Insurers must first assess their organizational readiness and develop a clear strategy aligned with business objectives. This includes prioritizing high-impact use cases and establishing a secure environment for iterative testing and scaling. The effective utilization of GenAI fundamentally depends on robust foundational capabilities: a sophisticated technical infrastructure, comprehensive central data assets, well-defined governance frameworks for both data and models, targeted talent development, and a clear operating model for data and AI initiatives.
By taking a holistic approach to GenAI adoption, insurers can drive operational efficiency and unlock new growth opportunities in the digital age. Success begins with a bold vision and willingness to embrace this transformative technology. Those who proactively invest in building strong foundations and necessary capabilities will be best positioned to realize GenAI's full potential in underwriting transformation.
Want to know more about how to leverage GenAI for underwriting operations? Learn more about our GenAI services on our website.








